PASSIVE HOUSE DESIGN
Passive House Design is a method of design and system or structure that uses natural energy to function rather than using electricity or fuel.
Sources of natural energy include sunlight, wind, temperature differences, and gravity. On the other end of it is Active Design. Which is a system or structure that uses or produces electricity.
Most of the time, when we reference passive design, it is with respect to infrastructure and architecture. To achieve Passive design there are many approaches that we can take.
The Main Four Approaches to Passive House Design
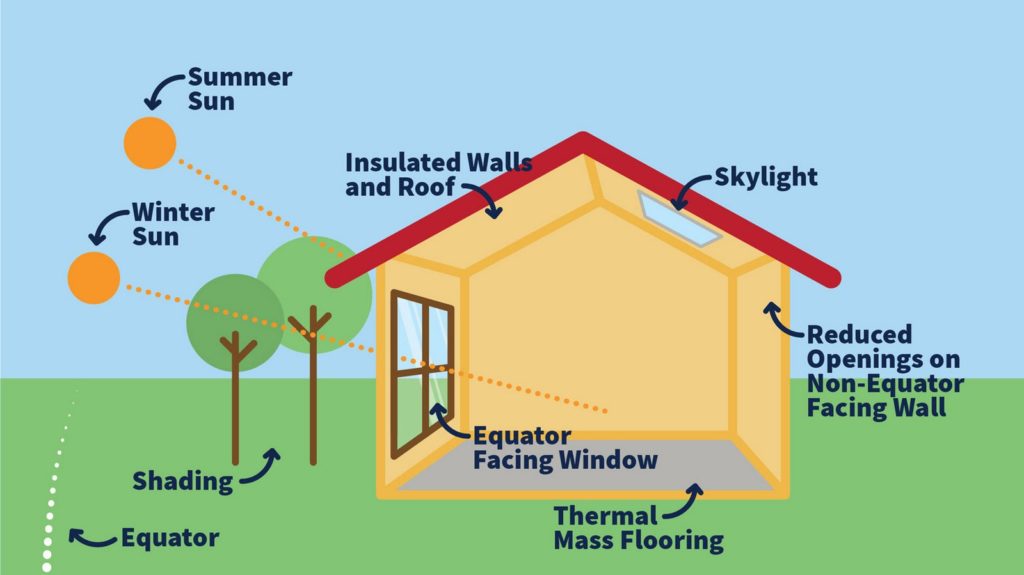
Natural Ventilation
Natural Ventilation is easier to achieve when the buildings are in climates with a more constant temperature throughout the year. It is also easier to accomplish this in a place that doesn’t have extremely high temperatures and below-freezing temperatures. When implementing natural ventilation into your design, you consider how air will move throughout the space. You must ensure it flows efficiently in and out of the area of focus without getting trapped. In order to achieve natural ventilation, a common strategy used is called Cross Ventilation, where a house has openings at opposite orientations.
Building Orientation
Is a crucial step in achieving a passive design. The designer must observe and consider site specifics to determine what the orientation of the home should be. This is where we find what direction gets the most sunlight consumption and exterior shades.
Once you have found that information, it helps the designers understand the shape and materials that will be best for an energy-efficient home. Most homes face either North or South to absorb the most sunlight. Adding cross-ventilation windows on those sides of the space allows more natural sunlight to enter.
Natural Lighting
Is another aspect to consider during the initial design phase. Not only is it imperative for the occupant’s health, but it affects the building and how efficient its energy consumption is. There are several things that come to play when determining energy efficiency from the windows and natural light. One of those is the type of windows used for what climate. For example, in hotter climates, you should use windows with low-E coating to exclude radiant heat.
Another factor would be the location of the window on the wall. Higher-placed windows allow the natural light to enter and spread throughout the space more consistently. During different seasons the sun hits the same wall in different ways; Which could mean if it isn’t in the proper location, it could be efficient during the summer but not the winter.
Insulation
Is a crucial part of the building and ensures its efficiency. A good passive design strategy would be to design the homes building envelope above what the energy code requires. To accomplish this, you add more insulation throughout the building envelope as well as different types of insulation, like rigid insulation.
Not only is consistent insulation imperative for cold regions, but it also enables the building envelope to resist the conductive flow of heat. Another benefit of no thermal bridges from wrapping the building in insulation is the elimination of indoor mold and improvement of air quality.
If you take these four methods into consideration during the design phase of your home, you will save money in producing a passive house design. However, renovating an existing home to create a passive home can still result in a cost-effective home.
Consulting a designer with passive house design experience for either the new build or renovation of your existing home can save you money in the long run while helping the planet at the same time.

Nehalem OR
United States
CALL OR TEXT: 503-746-3761